Real Estate Loans:
What are they?
A Real Estate Loan is a type of financing specifically designed to help businesses acquire, develop, or refinance real estate. These loans are often used for purchasing commercial properties, such as office buildings, warehouses, or retail spaces, but they can also be used for construction or renovation projects.
Here’s how it works: Real estate loans are provided by banks, credit unions, or other lending institutions. The property itself typically serves as collateral, meaning if the business fails to repay the loan, the lender can seize the property to recover their money. This setup makes real estate loans a relatively secure option for lenders, which can result in more favorable terms for borrowers, such as lower interest rates or longer repayment periods.
Because the property acts as collateral, lenders are more likely to offer large sums of money, making these loans ideal for substantial investments in real estate. However, qualifying for these loans can be more stringent, requiring a strong credit history, significant equity, and a clear plan for the property’s use or development.
How do I get one?
To qualify for a Real Estate Loan, businesses need to meet several requirements. Here are the key ones:
Property Type: The property must be a commercial real estate asset. Residential properties typically do not qualify unless they are intended for mixed-use, with significant commercial activity.
Business Purpose: The property must be used for business operations, such as offices, retail, or industrial use. Investment properties, where the primary intent is to rent out or sell the property, might have different loan options.
Good Credit: The business owner(s) generally need to have a solid credit history. Lenders want to see that the owner has a history of managing debts responsibly.
Down Payment: Borrowers typically need to provide a down payment, usually ranging from 10% to 30% of the property’s purchase price. This shows the lender that the borrower is financially committed to the property.
Collateral: The real estate itself usually serves as collateral for the loan. This means that if the borrower defaults, the lender can foreclose on the property.
Ability to Repay: The business must demonstrate the ability to repay the loan, often by showing financial statements, income projections, and tax returns. The lender will assess the property’s potential to generate income, especially if the loan is for a rental or leased property.
Environmental Assessments: For certain properties, lenders may require an environmental assessment to ensure there are no hazardous materials or other environmental issues that could affect the property’s value.
Appraisal: Lenders typically require a professional appraisal to confirm the property’s value, ensuring it justifies the loan amount.
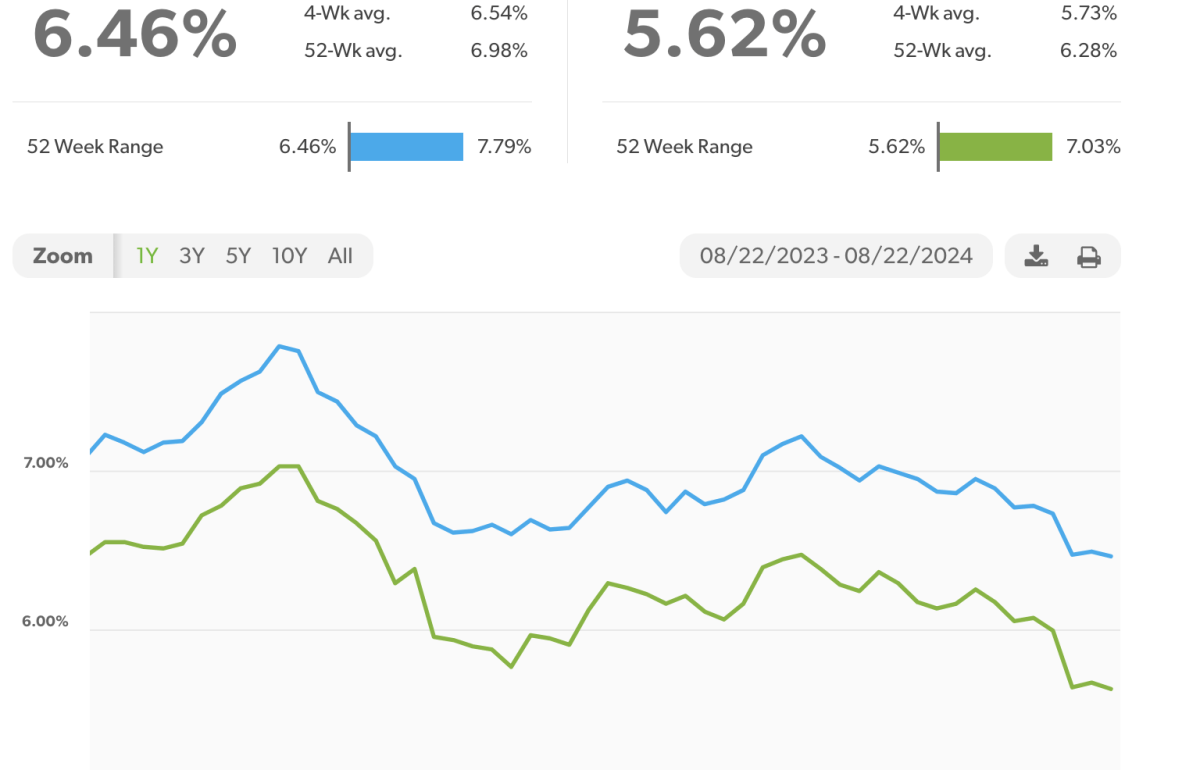
2024 Real Estate Loan Interest Rates:
Questions? You’re Covered
Typically, a credit score of 680 or higher is preferred, but this can vary based on the lender and the specific loan product
The process can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on the complexity of the deal and the specific requirements of the lender.
